MECHANICAL DESIGN LABORATORY
MEMB321
BELT FRICTION TESTER
LAB SESSION: Section 1
DATE PERFORMED: 1999
DATE DUE: 1999
GROUP No: **
AUTHOR***
GROUP MEMBERS:
Objective
2
Data and
observation
3
Analysis
and discussion
5
Conclusion
6
The main
objective of this experiment is to determine the coefficient of friction between
steel and belt ( Vee and Flat).
Procedure
a)
Two 1.25kg weight holder. The weight was hung onto
the cable.
b)
The belt was change to a vee belt.
c)
The end of T2 spring balance was inserted onto the 30 degrees peg on the
apparatus.
d)
The end of T1 spring balance was tighten by using the nut and bolt on the
apparatus.
e)
T1 and T2 values were recorded.
f)
The end at T1 spring balance was tighten more by using the nut and bolt
on the apparatus. T1 and T2 were recorded.
g)
Step f was repeated until 5 readings for t1 and t2 are obtained.
h)
Step c until g was repeated with the T2 spring balance being hooked onto
he 60,90,120 and 150 degrees peg.
i)
Step b i was repeated for flat belt.
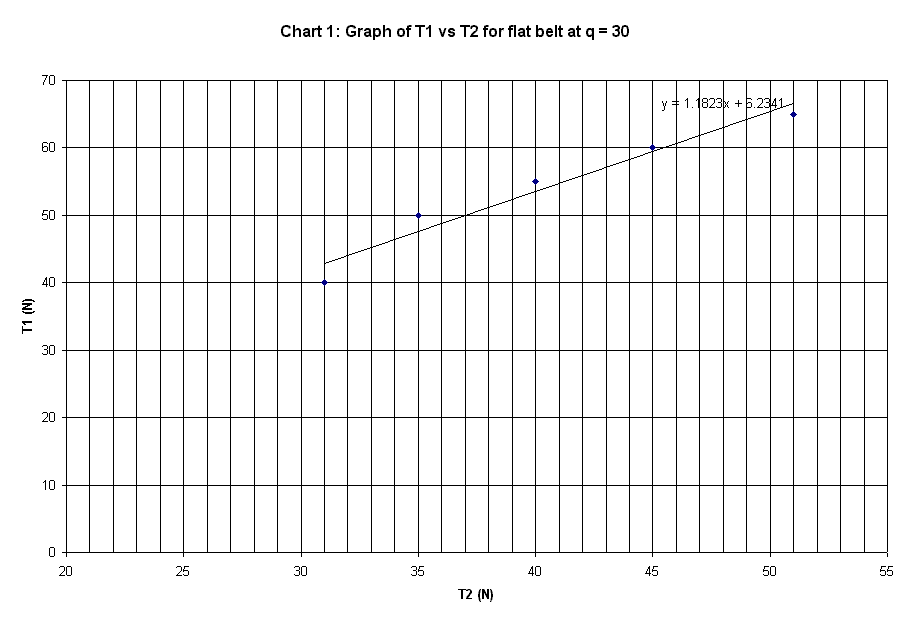
Flat
Belt
|
30 deg. |
peg |
|
|
|
60 deg. |
peg |
|
|
T1 |
T2 |
mu |
|
|
T1 |
T2 |
mu |
|
40 |
31 |
0.4868 |
|
|
80 |
75 |
0.0616 |
|
50 |
35 |
0.6812 |
|
|
90 |
80 |
0.1125 |
|
55 |
40 |
0.6082 |
|
|
95 |
86 |
0.095 |
|
60 |
45 |
0.5494 |
|
|
100 |
93 |
0.0693 |
|
65 |
51 |
0.4633 |
|
|
105 |
99 |
0.0562 |
|
Ave. m from table |
0.55778 |
|
|
Ave. m from table |
0.07892 |
||
|
Slope of plot |
1.1823 |
|
|
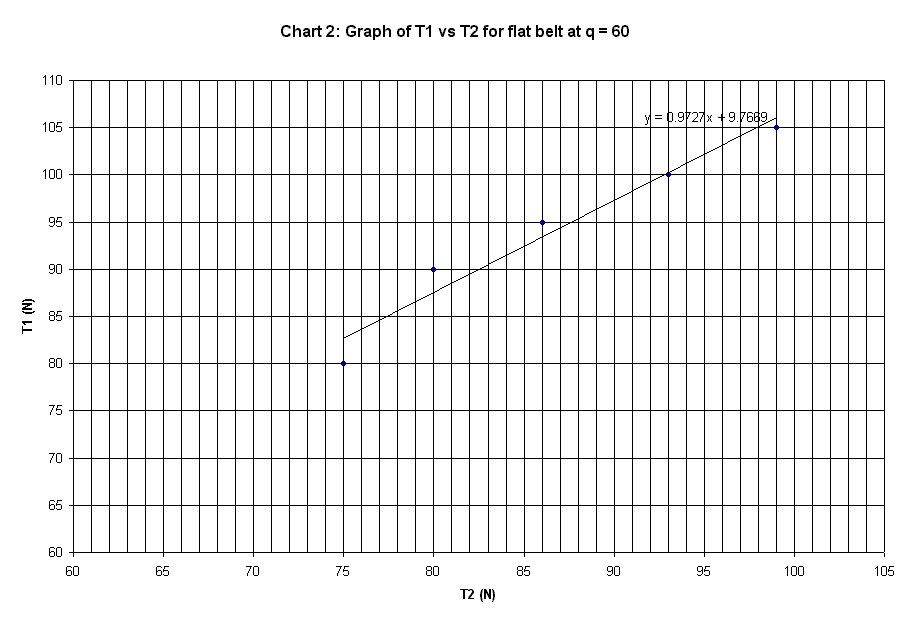
Slope of plot |
0.9727 |
||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
90 deg. |
peg |
|
|
|
120 deg. |
peg |
|
|
T1 |
T2 |
mu |
|
|
T1 |
T2 |
Mu |
|
60 |
49 |
0.1289 |
|
|
60 |
50 |
0.0871 |
|
65 |
53 |
0.1299 |
|
|
65 |
54 |
0.0885 |
|
70 |
59 |
0.1088 |
|
|
70 |
57 |
0.0981 |
|
80 |
65 |
0.1322 |
|
|
75 |
63 |
0.0832 |
|
85 |
71 |
0.1146 |
|
|
80 |
70 |
0.0638 |
|
Ave. m from table |
0.12288 |
|
|
Ave. m from table |
0.08414 |
||
|
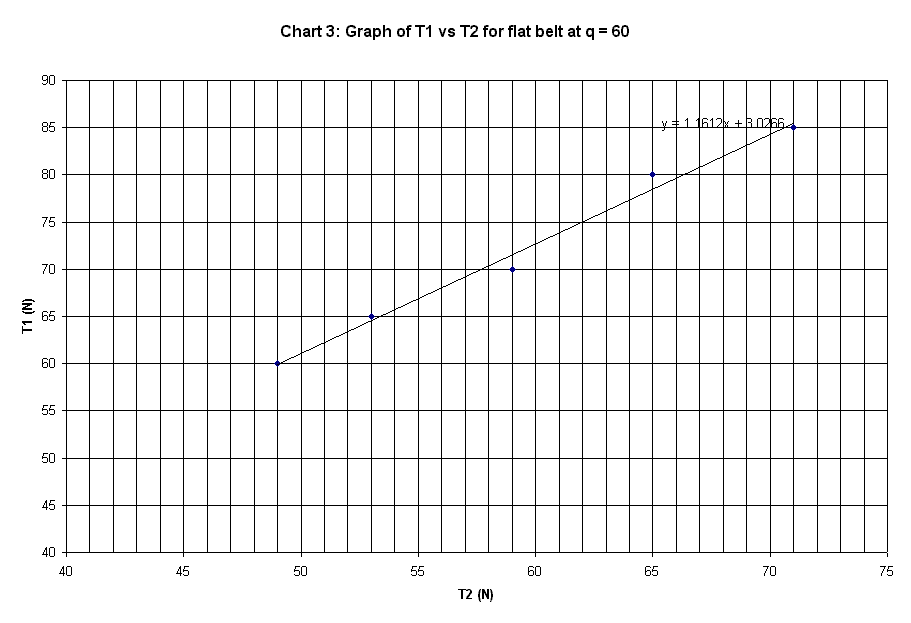
Slope of plot |
1.1612 |
|
|
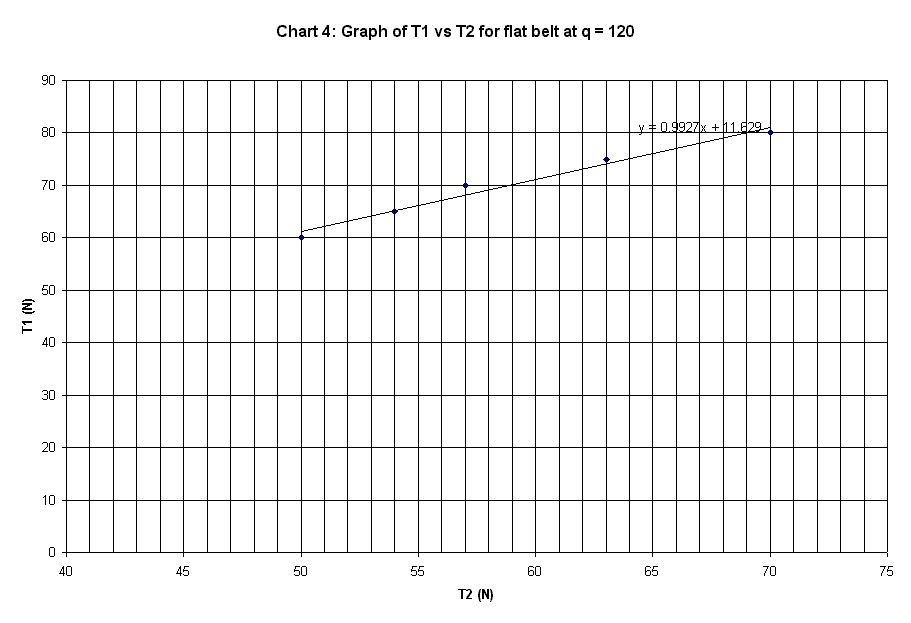
Slope of plot |
0.9927 |
||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
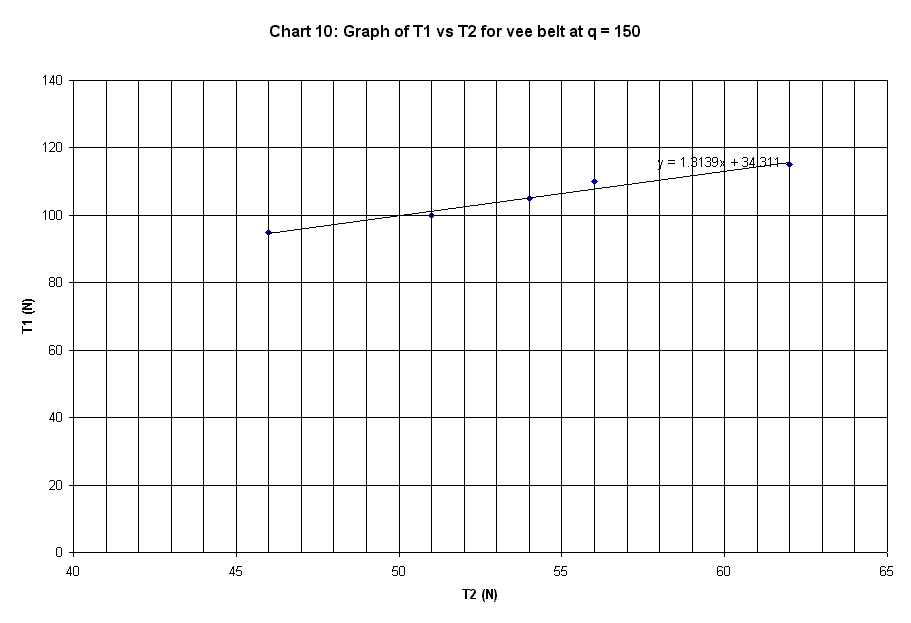
150 deg. |
peg |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
T1 |
T2 |
mu |
|
|
|
|
|
|
50 |
36 |
0.1255 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
55 |
46 |
0.0683 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
60 |
52 |
0.0547 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
70 |
60 |
0.0589 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
75 |
65 |
0.0547 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
Ave. m from table |
0.07242 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
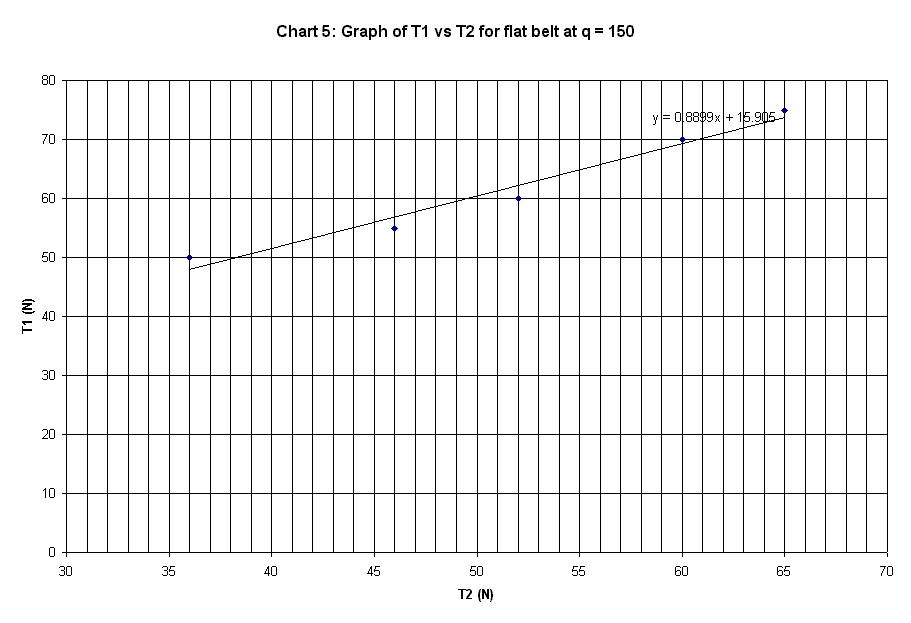
Slope of plot |
0.8899 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
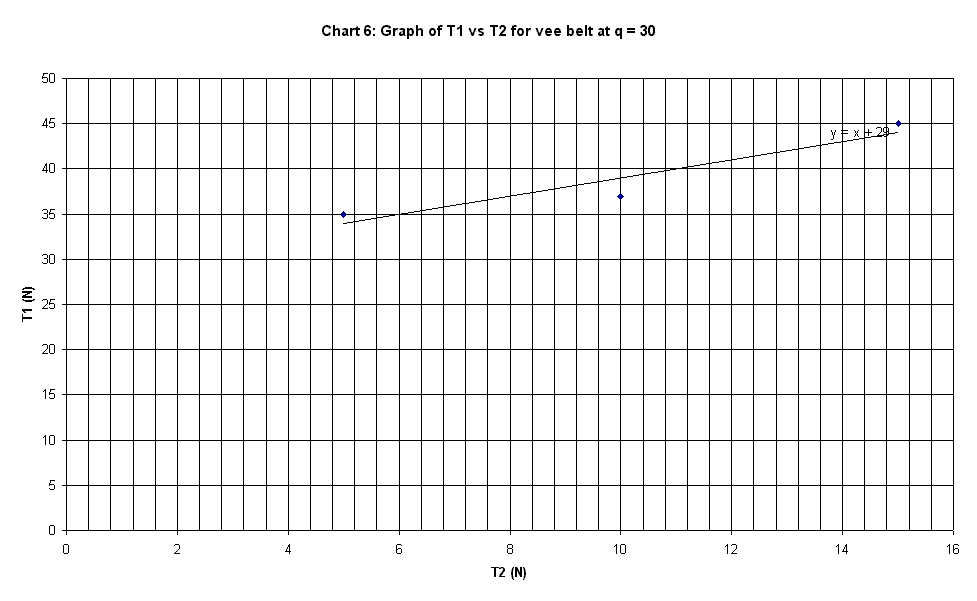
30 deg. |
peg |
|
|
|
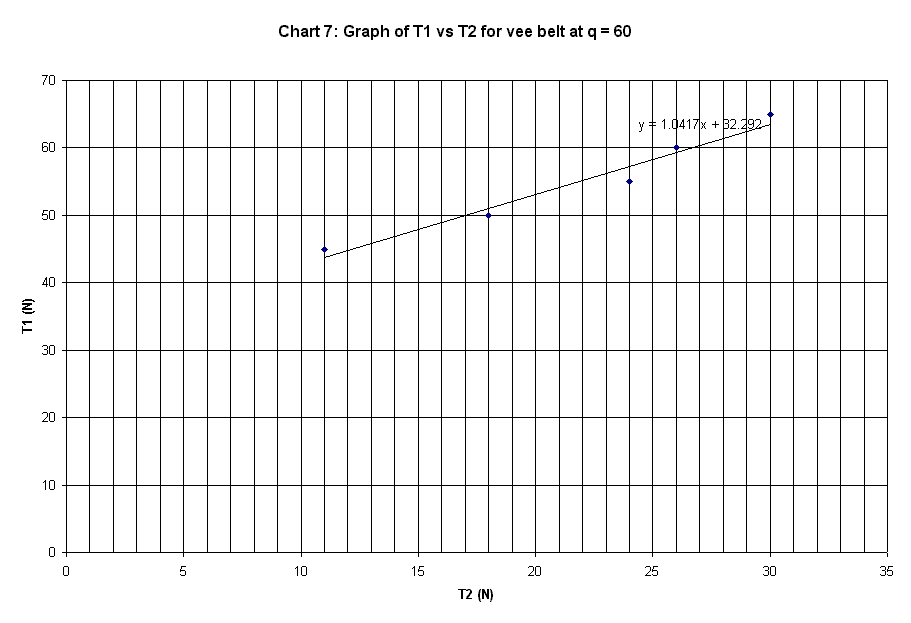
60 deg. |
peg |
|
|
T1 |
T2 |
mu |
|
|
T1 |
T2 |
mu |
|
35 |
5 |
1.2711 |
|
|
45 |
11 |
0.4601 |
|
37 |
10 |
0.8546 |
|
|
50 |
18 |
0.3337 |
|
45 |
15 |
0.7176 |
|
|
55 |
24 |
0.2708 |
|
50 |
20 |
0.5985 |
|
|
60 |
26 |
0.2731 |
|
55 |
22 |
0.5985 |
|
|
65 |
30 |
0.2525 |
|
Ave. m from table |
0.80806 |
|
|
Ave. m from table |
0.31804 |
||
|
Slope of plot |
1 |
|
|
Slope of plot |
1.0417 |
||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
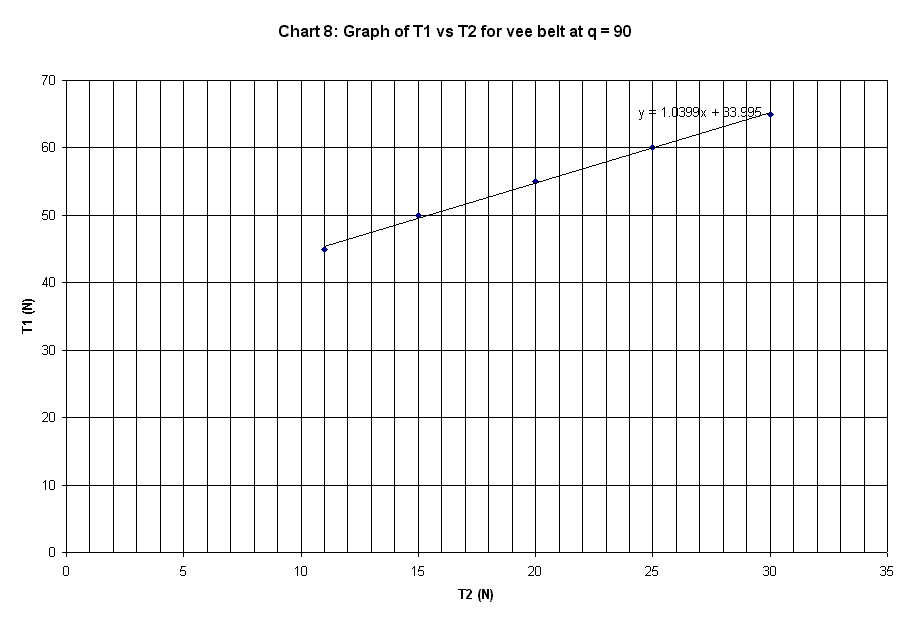
90 deg. |
peg |
|
|
|
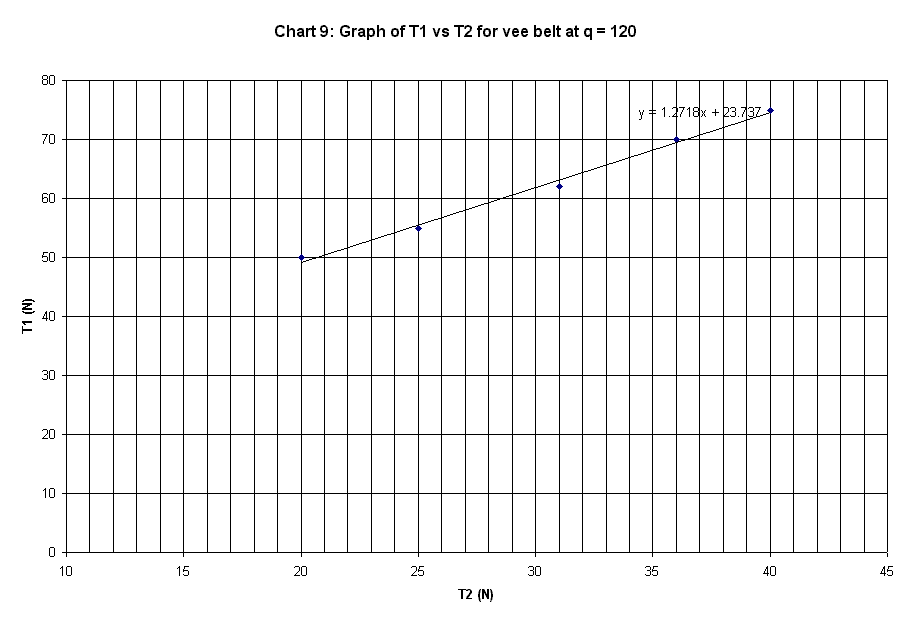
120 deg. |
peg |
|
|
T1 |
T2 |
mu |
|
|
T1 |
T2 |
mu |
|
45 |
11 |
0.3067 |
|
|
50 |
20 |
0.1496 |
|
50 |
15 |
0.2621 |
|
|
55 |
25 |
0.1288 |
|
55 |
20 |
0.2203 |
|
|
62 |
31 |
0.1132 |
|
60 |
25 |
0.1906 |
|
|
70 |
36 |
0.1086 |
|
65 |
30 |
0.1684 |
|
|
75 |
40 |
0.1027 |
|
Ave. m from table |
0.22962 |
|
|
Ave. m from table |
0.12058 |
||
|
Slope of plot |
1.0399 |
|
|
Slope of plot |
1.2718 |
||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
150 deg. |
peg |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
T1 |
T2 |
mu |
|
|
|
|
|
|
95 |
46 |
0.0947 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
100 |
51 |
0.088 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
105 |
54 |
0.0869 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
110 |
56 |
0.0882 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
115 |
62 |
0.0807 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
Ave. m from table |
0.0877 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Slope of plot |
1.3139 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
Analysis
and Discussion
1.
The coefficient of friction for each peg
are as given in the following table:
|
|
For Flat belt |
For Vee belt |
|
Angled peg |
Coefficient of
friction |
|
|
30 deg |
0.55778 |
0.80806 |
|
60 deg |
0.07892 |
0.31804 |
|
90 deg |
0.12288 |
0.22962 |
|
120 deg |
0.08414 |
0.12058 |
|
150 deg |
0.07242 |
0.0877 |
Table 1: The coefficient of
friction for each angled peg.
2.
From the experiment there are a few
friction, which has the same coefficient as in the table in the lab manual. For
flat belt at 90 degrees it has the same coefficient as greasy iron as the pulley
material with canvas stitched and cotton woven. This is also the sane as for vee
belt with 150 degrees peg. For v belt at 60 degrees peg have the same
coefficient as Iron steel for pulley and balata as the belt material, also
rubber covered belt material for iron steel and wood pulley. At vee belt 90
degrees peg the same coefficient is for canvas stitched belt material and wood
pulley.
3.
The graphs plotted in Chart 1 to 10 are
linear curve with positive slope. The slope of the graphs is the ratio of T1 /
T2.
4. The possible sources of error in the experiment are the twisting of the belt during the course of this experiment. The twisting causes inaccurate reading of the spring balance because some of the tension applied on the belt were applied to the twisted portion of the belt. Error while taking the reading can also occur because the spring does not have proper scales and it is hard to read it accurately.
Conclusion
This
experiment was successfully done and it is really give us an insight on how peg
angled can affect the coefficient of friction of the same belt and pulley.
The
data obtain does not match up so much with the table given in the manual. This
maybe due to calculation error and error while taking the reading of the
subjected force of the spring.
The main thing in this experiment is that we know how to calculate the
coefficient of friction of a given belt and pulley at a certain angle provided
we know the forces of T1 and T2. This experiment make us realize that we do not
need to use a different pulley or different belt in order to produce a desired
coefficient of friction, what we only need is to change the angle peg of the
belt to the pulley.